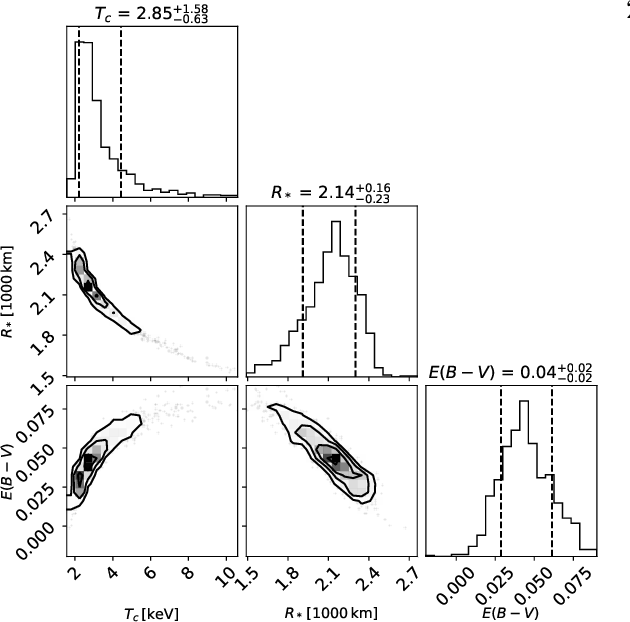
ZTF J1901 1458 (nicknamed Z; formally ZTF J190132.9 145808.7; Gaia ID 4506869128279648512) is a white dwarf, about 135 light years away roughly in the direction of Epsilon Aquilae, discovered by the Zwicky Transient Facility circa 2021. It is the most massive white dwarf yet found, having 1.35 times the mass of the Sun, nearly the largest expected mass for this type of object. Its radius is about 2,140 km (1,330 mi), about the size of Earth's Moon, and it rotates once every 7 minutes.
The object's extreme rate of spin is hard to explain without supposing ZTF J1901 1458 to be the result of a white dwarf merger, near the upper mass limit of a stable end product. Larger white dwarf mergers could be another mechanism of supernova production, which is not necessarily taken into account in how we have traditionally inferred dark energy from supernova observations.
See also
- List of white dwarfs
References